
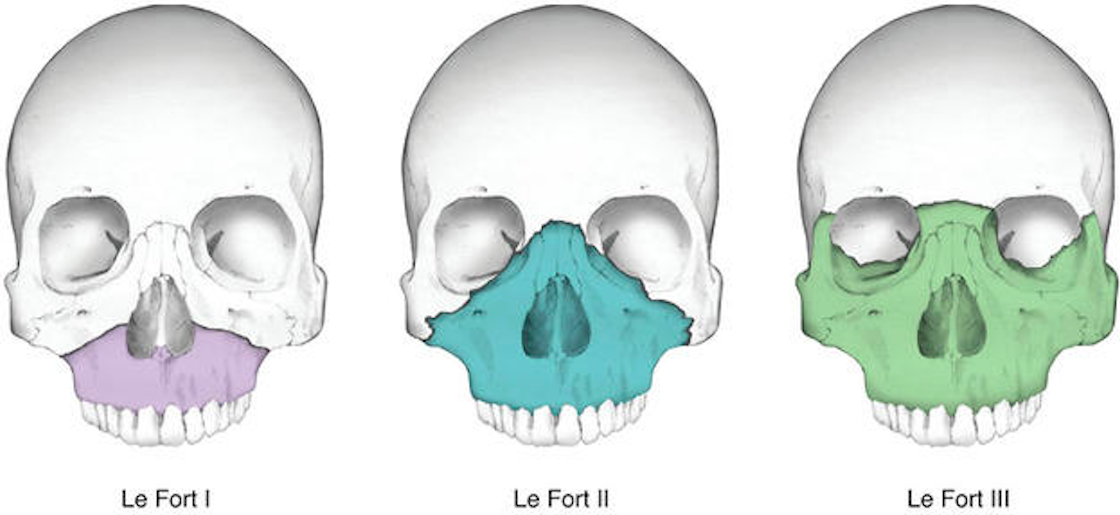
Sliker CW, Steenburg SD, Archer-Arroyo K.Experimental study of fractures of the upper jaw: a critique of the original papers published by René Le Fort. The classic reprint: experimental study of fractures of the upper jaw. Étude expérimentale sur les fractures de la machoire supérieure. Nouveau moyen de les reconnaitre dans les cas fréquents ou elles ne s’accompagnent pas de déplacement In: Archives générales de médecine, 1866,Vol.2, pp5-13 Des fractures des maxillaires supérieurs. At examination, only insignicant lesions of the alveolar border were found… Three blows with a club were applied directly to the front of the upper maxilla, with moderate force. The fracture extends from the nasal septum to the lateral pyriform rims, travels horizontally above the teeth apices, crosses below the zygomaticomaxillary junction, and traverses the pterygomaxillary junction to interrupt the pterygoid plates. fractures (lefort II, III) and some severe fractures of the nasal complex as. Le Fort I fractures (horizontal) This may result from a force of injury directed low on the maxillary alveolar rim in a downward direction. He determined that predictable patterns of fractures are the result of certain types of injuries, and concluded that there are three predominant types of mid-face fractures.Įxperiment I: Female, approximately 50 years old. In certain types of extensive fractures the midfacial bones are crushed or. Le Fort used intact cadaver heads, and delivered blunt forces of varying degrees of magnitude and direction. where they have the least resistance.ġ901 – René Le Fort described fracture classifications based on experiments conducted in 1900 by dropping bricks on 35 cadavers and observing the pattern of maxillary fractures. When a violent blow is struck backward on the face, as if one wanted to push in the part of the upper jaw lying below the nostrils, a transverse fracture is produced which passes about one centimetre below the malar bone and extends through the pterygoid processes the latter processes are always fractured at the level of thelower end of the pterygomaxillary fissure i.e. 1866 – Alphonse Guérin (1816-1895) showed that it was possible to diagnose fractures of the maxilla which in the past might have been missed because of their lack of displacement.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
